The BPAT assessment process provides multiple benefits for breeding institutions:-
- Opportunity for institution selfreflection on their initiatives and capabilities and to prioritize opportunities for improvement
- Institution can align with donors and other key stakeholders on current capabilities
- BPAT can identify improvement opportunities in need of support for future programmatic initiatives
Key elements of BPAT

The breeding program assessment tool (BPAT) is based on the key elements that drive a public sector breeding program’s ability to achieve higher rates of genetic gain, including: breeding-specific execution and impact factors and enabler support factors of strategic planning, budgeting, and performance management.
Each institution is assigned a 1-4 score per question based on the organization’s current capabilities.
The tool is anchored by a perspective on best practices in public and private sector breeding programs.
The assessment will contribute to a strategic plan for the institution to achieve higher rates of genetic gain.
BPAT is a tool to outline an improvement plan so that all investments are successful in achieving those objectives.
There is no “bad” score but rather a process to identify strengths and weaknesses. Accurate scoring is critical to ensure that gaps can be addressed in the grant making process. Institutions are encouraged also to use the tool for self-improvement regardless of donor direction.
- The assessment process has been developed and tested with experienced breeders.
- The tool has been developed and refined by a team of former public and private sector breeders, agriculture and change management-focused consultants, and BMGF staff.
- The team conducted a series of interviews with public and private sector breeding organizations across four continents
BPAT Process
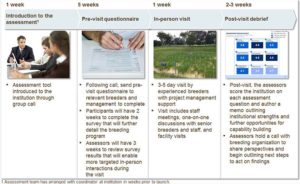 There are four components to the assessment process (which typically spans 10 to 12 weeks):
There are four components to the assessment process (which typically spans 10 to 12 weeks):
1) Introducing institutions to the assessment process: Introduce the assessment process to the institution;
2) Pre-visit questionnaire: Collect information about the institution and its breeding programs prior to the in-person visit through pre-visit questionnaires;
3) In-person visit: Visit the institution to meet with the management team, breeders and other scientists, and to tour the institution’s infrastructure and field facilitates ;
4) Post-visit debrief: Follow up with the institution through an assessment scorecard and memorandum explaining observations and offering improvement recommendations .
Assessment team on-site visit
A typical assessment team will consist of consultants (assessors), whose combined skill sets provide the ability to evaluate technical aspects of the breeding program, evaluate enablers across the institution, coordinate a well-run process, and provide meaningful feedback to the institution being assessed as well as the donors/sponsors of BPAT.
The assessors will review the returned pre-visit questionnaires and use the information to highlight specific questions, concerns, or areas that especially need attention to understand during the visit, and to help them complete the assessment matrix (on-site questionnaire).
During the on-site visit, the assessment team will:-
- hold a group session at the beginning of the visit
- hold individual interviews
- tour the institution’s fields and facilities including crossing operations, selection nurseries, yield trials, seed production facilities including screenhouses, glasshouses, screening programs, seed storage, quality testing and biotechnology laboratories
- hold a group session at the end of the visit
The on-site questionnaire can be downloaded from the BPAT Project > Tools page.
Please note that you need to be registered (have an account) and logged on, to be able to access the Tools page.
Post-visit assessment score and report
 The assessors will write a corresponding visit summary report to complement the assessment.
The assessors will write a corresponding visit summary report to complement the assessment.
The report will include a commentary based on the nine components of the on-site assessment, highlighting the strengths and the major opportunities for improvement.
In addition, it will show the prioritization of critical and medium priority recommended actions for the organization.
